十一、I/O编程
IO在计算机中指Input/Output,也就是输入和输出 官方文档
1. 文件的打开和关闭
# 打开文件并返回一个文件对象,关键字参数encoding可设置编码格式
file = open('./source/text.txt', encoding='utf-8')
# 读取文件内容 read()方法中可传入参数,设置读取字符的数量,默认是-1,读取全部
print(file.read(1024))
# 关闭文件
file.close()
with...as语句:
with open('./source/text.txt', encoding='utf-8') as file:
text = file.read()
print(text)
file.read()
执行效果:
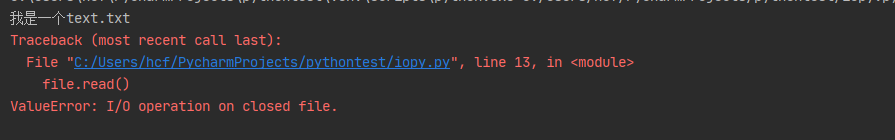
使用
with...as语句操作的文件只能在with中使用,一旦语句结束,文件就会自动close(),不需要手动调用close()方法
2. 读取大文件
with open('source/text2.txt', encoding='utf-8') as file:
while True:
content = file.read(1024)
# 逐行读取
# content = file.readline()
# 循环读取,content为空时退出循环
if not content:
print('读取完毕')
break
print(content)
3. 文件的写入
# with open('source/text.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
with open('source/text.txt', mode='w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
# 可以分多次向文件写入内容,并且内容不会自动换行
file.write('hello kitty (*^▽^*)\n')
file.write('hello2 kitty (*^▽^*)\n')
file.write('hello3 kitty (*^▽^*)\n')
使用
open()方法打开的文件默认是只读模式,想要写入必须设置类型mode(第二个参数)
r:表示只读,默认值,文件不存在会报错
w:表示可写的,使用w写入文件时,如果文件不存在则会创建文件,如果文件存在则会覆盖原来文件内容
a: 写入,如果文件存在则在末尾追加
4. tell()和seek()
with open('source/text2.txt', mode='rb') as file:
# seek()修改当前读取到的位置
file.seek(55, 0)
# tell()当前读取到的位置
print(file.tell())
print(file.read(100))
tell():查看当前文件读取的位置
seek():修改当前文件读取的位置,参数:
- 要切换到的位置
- 计算位置的方式,可选值:0(从头计算,默认值) 1(从当前位置计算) 2(从最后计算)
注:seek()是按照字节数来定位的,utf-8下一个中文字符是三个字节,如果设置的位置无法取到一个完整的中文字符,则会报错
5. 文件的其他操作
# 文件的其他操作
import os
from pprint import pprint
# 获取指定目录的目录结构,返回list。可传入一个路径参数,不传入的话默认当前目录
listdir = os.listdir()
pprint(listdir)
# 获取当前所在目录的路径
pprint(os.getcwd())
# 切换当前所在目录,相当于cd
os.chdir('c:/')
pprint(os.getcwd())
# 创建目录
os.mkdir('a')
# 删除目录
os.rmdir('a')
# 删除文件
os.remove('source/aa.txt')
# 重命名,参数可以是一个完整的路径
os.rename('source/aa.txt','source/bb.txt')